Quick intro from Jim Benson:
We've asked Chris Hefley from Leankit to write a series of posts showing how to integrate tools many of us use everyday with our Personal Kanban. These are fairly technical posts, but also very powerful ones.
In this first post, Chris mentions that his aim is to keep his inbox at zero by taking action items and moving them directly to his Personal Kanban. Tonianne and I have also noticed that we also tend to act on emails the moment they arrive. This means that we allow email to interrupt our flow of work - then we get to the end of the day and are disappointed by how we let those interruptions derail our day.
Chris lays out a simple mechanism to move emails into your Leankit Personal Kanban that can both clean out your inbox and give some of those interruptions their proper priority. Also, I've turned Chris' post into a video which is at the bottom.
Take it away, Chris
-----------
I aspire to keep my inbox at zero. About once every couple of weeks, I actually get there. I’ve got several tools that I use to help me with that, including moving emails to my Personal Kanban board in LeanKit.
LeanKit has a connector available for Zapier, a cloud based integration hub. Zapier provides hundreds more connectors with other applications, which makes it very easy to connect LeanKit with Gmail, ZenDesk, BugZilla, BaseCamp, and many more.In this article, I’ll show you how to set up a “Zap” to create a LeanKit card based on an email in Gmail, complete with a link back to the original email, so that you can get that “to do” item onto your Kanban board and out of your inbox.First, you’ll need to go to Zapier.com and create an account. There’s a free account that should work just fine, and if you need more integrations or faster synchronization you can upgrade later.Once you’ve created your account, you’ll be asked to create your first “Zap”, and presented with the screen below:
On the Trigger (left) side, choose Gmail, and choose “New Thread”.
On the Action side (right side) choose LeanKit and “New-Add Card” for the action.So that when a new Thread is created in Gmail that fits the criteria we will add later, it will create a matching card in LeanKit.
Follow the steps in Zapier to set up your Gmail account:
…and your LeanKit account.
Now, in a separate browser tab, go into your gmail account, open an email, and create a Label called “lk” (or something similar) for that email. (Help for how to create a label in Gmail: https://support.google.com/mail/answer/118708?hl=en)
Back in Zapier, in the filter for your Gmail Trigger, choose the “lk” label you created in the previous step (it could take a few minutes for the label to show up after you’ve created it. If you don’t see it after a few minutes, try saving your “Zap” incomplete, and then coming back to this step.)
In Zapier, Choose the LeanKit board you’d like to add cards to. This will allow you to select from any board in your LeanKit account (that you have access to with your login).
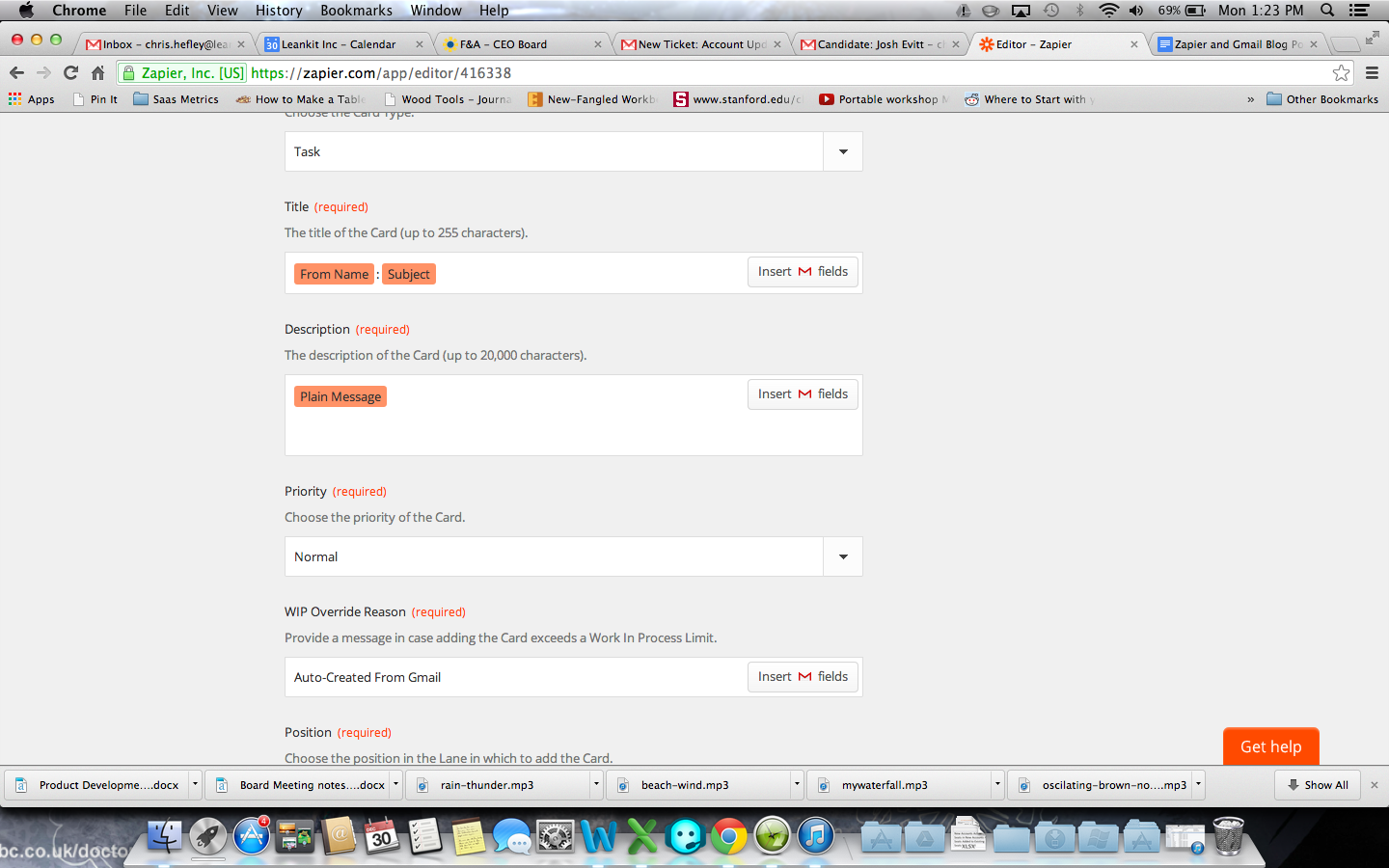
After selecting the Board, you’ll be able to select the lane you want new cards added to, and the Card Type you want for your new cards.
For the Card Title field, add the Gmail fields “From Name” and “Subject”, and add “Plain Message” to the description field.
You can also add “ThreadURL” to the Description field if you’re using Basic or Team edition to provide a link back to the email. Or follow the instructions further down to add the link to the card header if you’re using Portfolio edition.
Test it like so:
If you’re using LeanKit Portfolio Edition, you can use the “External Card ID” field. Add “ThreadID” to this field from the list of available Gmail fields.
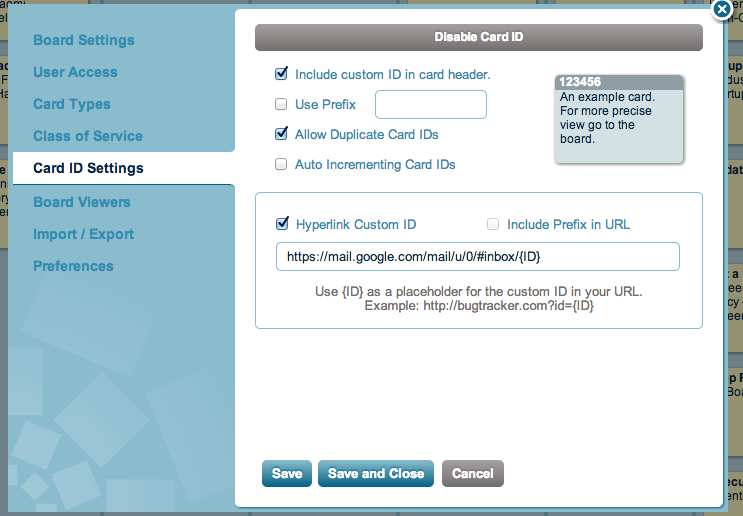
Open your LeanKit board in a new browser tab, and in the settings for your leankit board, enable Card ID, and set it up as shown below. The field is where the Gmail ThreadID will go. (Check the gmail message url by opening an email in your browser and confirming the format of the url shown below for the email).
Now, the link to the original thread will appear in the header of the card, allowing you to quickly jump back there without opening the card to view the description.
That should do it. You can test the Zap and turn it on in Zapier. Now, all you have to do is label a message in Gmail with “lk” and then archive it to get it out of your inbox. The next time the Zapier sync process runs, it will pick up that email and create a LeanKit card for it.